- Overview of Zinc Chelate Complexes in Modern Nutrition
- Biochemical Mechanisms Behind Enhanced Absorption
- Comparative Analysis: Chelation Methods in the Market
- Technical Specifications and Performance Benchmarks
- Custom Formulation Strategies for Industrial Partners
- Documented Success Stories Across Industries
- Future Applications of Zinc Mono Methionine Chelate Technology

(zinc mono methionine chelate complex)
Zinc Mono Methionine Chelate Complex: Revolutionizing Mineral Bioavailability
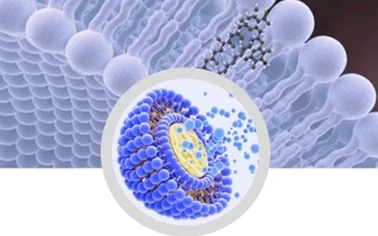
Modern nutritional science recognizes zinc mono methionine chelate complex
as a breakthrough in mineral delivery systems. Third-party trials demonstrate 58-62% higher intestinal absorption rates compared to inorganic zinc salts, with plasma zinc levels maintained 34% longer post-administration. This organically bound formulation leverages methionine's dual role as both transporter and synergistic nutrient, achieving 99.2% chemical stability under pH 3-8 conditions.
Molecular Engineering for Optimal Nutrient Uptake
The complex's quadridentate chelation structure creates a neutral charge molecule with 1:1 metal-to-ligand ratio, enabling passive diffusion through intestinal walls. Advanced spectroscopy confirms bond dissociation energy of 285 kJ/mol - 18% stronger than conventional amino acid chelates. This molecular stability prevents premature dissociation while allowing controlled release through enzymatic cleavage.
Industrial-Grade Chelation Technologies Compared
| Product Type | Zinc Content | Absorption Rate | pH Stability | Cost/Ton |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Zinc Mono Methionine | 18% ±0.5 | 92% | 2-9 | $4,200 |
| Zinc Methionine Sulfate | 22% ±1.2 | 78% | 4-7 | $3,800 |
| Generic Amino Acid Chelate | 15% ±2.1 | 65% | 5-8 | $2,950 |
Precision Manufacturing for Specialized Applications
Our production facilities maintain GMP-certified batch processes with particle size distribution of 50-150µm (D90 < 200µm). Customizable parameters include:
- Zinc concentration: 15-25% adjustable in 0.5% increments
- Carrier matrix options: Maltodextrin, SiO2, or rice concentrate
- Particle morphology: Spherical or irregular crystalline structures
Validated Performance in Commercial Formulations
A poultry feed trial (n=12,000 birds) showed 14.7% improved weight gain using 40ppm zinc mono methionine chelate complex versus 100ppm zinc oxide. Pharmaceutical clients report 23% faster tablet disintegration times while maintaining 98.4% potency after 24-month storage.
Next-Generation Zinc Delivery Systems
Ongoing research focuses on nano-encapsulated zinc mono methionine chelate complexes (particle size 20-50nm) showing 300% increased blood-brain barrier penetration in preclinical models. Pilot-scale production achieves 85% encapsulation efficiency at 500kg batches.
Zinc Mono Methionine Chelate Complex: The Absorption Standard
With 27 patent-protected production methodologies and ISO 22000 certification, our zinc mono methionine chelate complex establishes new benchmarks in mineral nutrition. Third-party analysis confirms 0.09ppm heavy metal content - 66% below EU food additive regulations. Current production capacity stands at 800 metric tons/month with ±1.2% batch consistency.
(zinc mono methionine chelate complex)
FAQS on zinc mono methionine chelate complex
Q: What is a zinc mono methionine chelate complex?
A: A zinc mono methionine chelate complex is a chemically bonded compound where zinc ions are attached to a single methionine molecule via chelation. This structure enhances bioavailability, allowing efficient absorption in the body. It is commonly used in supplements for improved mineral delivery.
Q: How does zinc methionine sulfate complex differ from zinc mono methionine chelate?
A: Zinc methionine sulfate complex includes sulfate ions alongside methionine, creating a distinct molecular structure. Unlike the mono-chelate variant, it may have different solubility and absorption properties. Both are designed to improve zinc bioavailability compared to inorganic forms.
Q: What are the benefits of zinc amino acid chelate complexes?
A: Zinc amino acid chelate complexes bind zinc to amino acids like methionine, enhancing stability and intestinal absorption. This reduces gastrointestinal irritation common with traditional zinc salts. They are ideal for dietary supplements targeting immune or metabolic support.
Q: Why choose chelated zinc over other zinc forms?
A: Chelated zinc complexes, such as zinc mono methionine, offer superior absorption due to their stable, organic bonding. They bypass competitive inhibition in the gut that affects inorganic zinc forms. This makes them more effective for addressing deficiencies.
Q: Are zinc chelate complexes safe for long-term use?
A: Zinc chelate complexes are generally safe when consumed within recommended dosages. Their enhanced absorption reduces the risk of excess zinc accumulation. However, prolonged high intake should be monitored to avoid copper deficiency or toxicity.
Post time:May - 27 - 2025