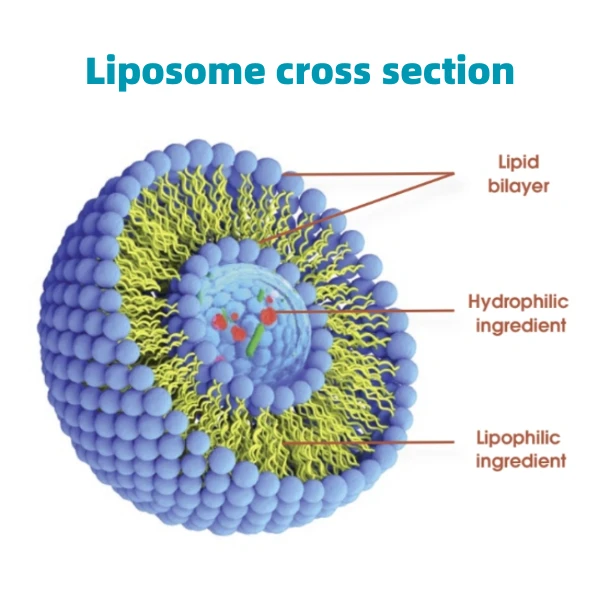
1. Place the prepared plant material into a clean glass jar, filling it about two-thirds full. 2. Pour your chosen solvent over the plant material until it is completely submerged. Ensure there's at least an inch or two of extra solvent above the plant material. 3. Seal the jar tightly to prevent evaporation and contamination. 4. Store the jar in a cool, dark place to prevent degradation by heat or light. 5. Allow the mixture to steep for 4-6 weeks, shaking the jar gently every few days to ensure the plant material is evenly exposed to the solvent. Filtration and Storage Once the extraction period is over, use a fine mesh strainer or cheesecloth to strain the liquid into a clean vessel, ensuring all plant material is filtered out. To further clarify the extract, consider using a coffee filter or tincture press as a second filtration step. Transfer the final extract into a dark glass bottle to protect it from light, which can degrade the quality over time. Label the bottle with the date and type of extract for easy reference. Store in a cool, dry place to maximize shelf life. Applications and Safety Before using your homemade plant extract, it's prudent to perform a patch test, especially with skincare applications, to ensure there's no adverse reaction. Plant extracts can be potent, so always consider the appropriate dilution based on their application. Follow expert resources or consult with a professional for specific guidance on dosage and application methods. In conclusion, making plant extracts requires a balance of scientific rigour and an appreciation for natural processes. As you develop your skills and understanding, you'll be able to create high-quality, effective extracts tailored to your needs. This ancient craft, enriched by modern knowledge and standards, allows one to engage closely with nature, creating a profound connection through tangible, beneficial products.
Post time:Jan - 11 - 2025